Rhinoplasty(Nose Reshaping) for Experts
Nose Reshaping / Rhinoplasty is an excellent and effective tool to achieve facial feminization in candidates undergoing male to female (MTF) gender affirmation (sex change) surgery.
Difference between Male Nose and Female Nose
Male nose is generally larger and wider than female nose which is usually smaller and slightly shorter. From front view female nose is narrower and have smaller nostrils with less flaring of nostrils. The tip is blunter in females than in males.
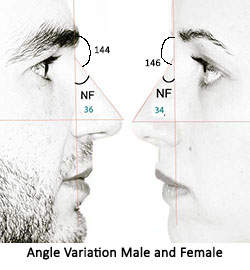
In side / lateral view: Angle at the base of nose (Naso- Frontal Angle i. e. NFA ) is less in females (340) as compared to male nose (36 0 ) . It means base of female nose is usually more upwards than in males (This indirectly corresponds to the vertical inclination of forehead).
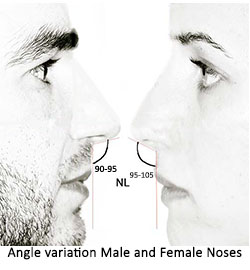
Female nose has wide angle between columella and upper lip (Nasolabial angle or NLA)- it is 100-103 degree in males and 105-108 degree in females.
A narrower less projected dorsum(decreased naso-frontal angle) without any hump , upward rotated tip( increased nasolabial angle) with supra-tip break is the hallmark of a feminine nose.
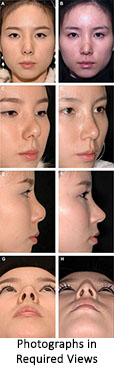
Systemic nasal analysis is a must to achieve the goal of nose feminisation. After through analysis rhinoplasty work sheet is planned. Rhinoplasty worksheet is the foundation for a focused feminizing rhinoplasty approach .This is done after pt’s nasal and facial photographs evaluation. Evaluation of these nasal and facial photographs is indispensable step for planning. For this photographs are taken in standard 6 views
| Area | Assessed Anatomy | Operative Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Nasofrontal angle position | ||
| Bony pyramid | ||
| Upper lateral cartilages | ||
| Supratip area | ||
| Nasal tip | ||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
| Alae | ||
|
||
|
||
|
||
| Alar-columellar relationship | ||
| Internal Nasal examination | ||
| Internal nasal valves | ||
| Septum | ||
| Turbinates |
A detailed aesthetic analysis includes a 10 point plan as follows:-
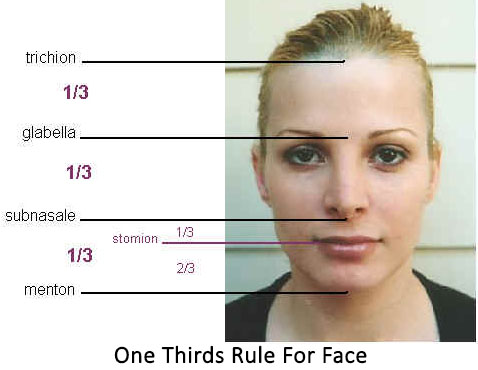
Face is divided into thirds by transverse lines, at mentum (chin), subnasale (base of columella), brow at supra orbital rims (glabella) and at hair line (also called as trichion)
A line is drawn from the mid glabellar area to the menton. It should bisect the nasal bridge, and upper lip. Any sign of nasal deviation is noted.

Dorsum of nose is defined and outlined by two lines extending from inner angles of eyebrows till tip defining points.
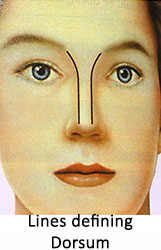
Width of bony base is about of the alar base. If it is wider than this will require mobilization of bones (osteotomies) to narrow the dorsum to achieve feminine look.
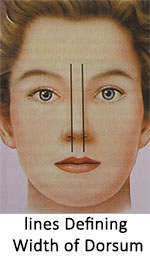
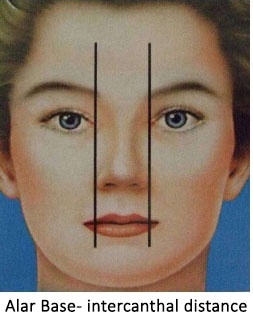
Alar width (width of nostrils) is approximately equals the distance between inner corners of the eyes (intercanthal distance). Wider alar area will need narrowing of alar base to look feminine.
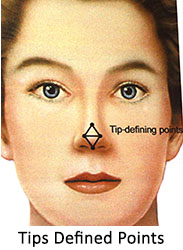
Normal female nose has a supratip break area. Lines connecting the tip defining poins to supratip break above and columello-lobular angle below form two equilateral triangles.Exact shape of tip and rotation of tip is extremely important to achieve a feminine nose.
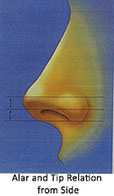
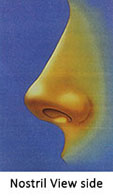
Relationship of ala and columella is important. Normal relationship gives a “seagull” appearance.Distance between the lines through tip defining points, through alar rims, and through tip defining points should be equal. Outline of nostril from sides should be oval.
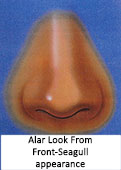
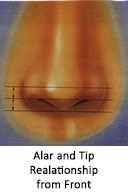
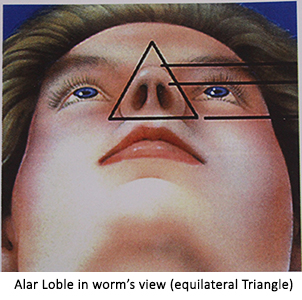
In worm’ view (also called as basal view i.e, looking to the nostrils from below)- Outline of nose should form an equilateral triangle . This indirectly provides the clue regarding extent of lift of nasal tip required to achieve feminization.
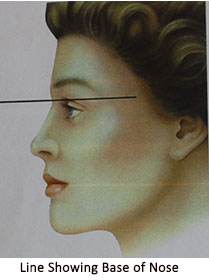
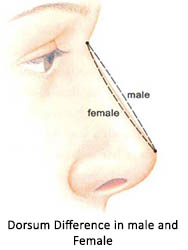
Assessment of dorsum (Side view)- The level of nose and naso-frontal angle is noted (this shows overall inclination of nose with the forehead) and is an important factor for gender recognition. The base of nose(deepest portion of naso frontal angle, also called as root of nose) should lie between upper lash line and supra-tarsal fold (upper eyelid fold) while patient looks straight. The naso frontal angle is more in males (36 0, corresponding angle being 1440) than in females ( 340 with corresponding angle being 1460). In that way the dorsum is approximately 2 mm behind and parallel to a line from just above naso frontal angle to the lip. In male nose, dorsum is little higher(forward).
Assessment of tip projection and tip rotation- Tip rotation is defined by Nasolabial angle. The angle is made by a line drawn through most anterior and posterior edges of the nostrils and a plumb line vertically dropped from glabellar point. This angle is larger in females (about 95-105, average being 100 degrees) than in males (90-95 degrees) . IT MEANS THAT UPWARD ROTATED TIP WITH SLIGHT SUPRATIP BREAK IS THE HALL MARK OF A FEMININE NOSE.
Surgical option: Rhinoplasty
Rhinoplasty, either closed or open rhinoplasty to make a feminine nose is one of the most rewarding procedure. In this the dorsal hump is corrected, female nasofrontal angle is achieved and the tip is made more feminine (turning it little up) according to the facial profile. A longer chiseled out face may need a straight bridge to look more natural.
Operative Plan and Technique- After meticulous analysis of face and facial photographs, the operative plan is finalized which obviously includes intraoperative analysis and further plan.
The Sequence and Rationale-
- Anesthesia- General anesthesia / Local with sedation.
- Incision- Trans columellar or inside the nostrils.
- Skin elevation and exposure of osteo-cartilaginous framework including lower lateral cartilages with creation of a pocket on dorsum till desired position of root of nose.
- Intra-operative assessment and diagnosis and any alteration in plan if needed.
- Judicious thinning of lobular skin from inside.
- Cephalic trim of lower lateral cartilages if indicated.
- Assessment of tip rotation and projection. Tip is made either with domal sutures and or with cartilage grafts/columellar strut. In this way the required tip projection and rotation is achieved.
- Dorsum reduction or augmentation as per need- Invariably dorsal definition and feminine root position is achieved with a cartilage graft (the source being nasal septum, conchal cartilage or rib cartilage). The cartilage being autogenous and natural tissue is considered safe.
If a hump is present, reduction is required before inserting the cartilage. Occasionally only hump reduction is sufficient. - Final inspection is done for any irregularities over the dorsum and lobule and any other correction if required is carried out.
- The incision is closed.
- Osteotomies are carried out to narrow the wider dorsum.
- Alar base width is reassessed. Wider alar base needs alar base reduction.
- Depressor septi muscles in upper buccal area are transposed to give an addition pout to lip as per need.
- Splint and dressing is done and a nasal pack is put if required.
- Recovery Time: Back to work within 7 days. Sometimes you may need a dressing over nose for about 2 to 3 weeks.
- Longevity of Results: Permanent
Ancillary procedures which may be carried out along with nose job:
Hair transplant, Face lift, Blepharoplasty, Fat grafting, Malar augmentation, Chin implant, Buccal fat pad removal, Dimple creation, Defining the jaw line, Double chin correction, Correction of prominent jaws













